Boost Power Module: Efficient Voltage Step-Up Solutions for Modern Electronics
May 14,2025
By:Epoch
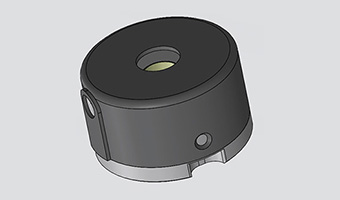
A boost power module is a specialized DC-DC converter designed to increase (or “boost”) a lower input voltage to a higher output voltage efficiently and reliably. These modules are essential in applications where the supply voltage is insufficient for the load requirements, such as battery-powered devices, renewable energy systems, electric vehicles, and telecommunications equipment.
How Does a Boost Power Module Work?
The core principle of a boost power module relies on energy storage in an inductor and controlled switching to increase voltage. When the internal switch (usually a MOSFET) is closed, current flows through the inductor, storing energy in its magnetic field. When the switch opens, the inductor releases this energy, adding to the input voltage and resulting in a higher output voltage than the input.
A blocking diode prevents the output from discharging back when the switch is closed, and an output capacitor smooths voltage ripple, ensuring a steady DC output. The output voltage is controlled by adjusting the duty cycle (the ratio of switch-on time to the total switching period), with the ideal output voltage given by:
where is the duty cycle (0 < D < 1).
Key Advantages of Boost Power Modules
· High Efficiency: Boost modules minimize energy loss by using switching techniques and synchronous rectification, often achieving efficiencies above 90%.
· Compact Size: Integration of inductors and switching elements into modules reduces board space, ideal for portable and embedded systems.
· Wide Input Voltage Range: Suitable for applications with variable or low input voltages, such as battery-powered devices or solar panels.
· Stable Output Voltage: Maintains consistent voltage despite input fluctuations or varying load conditions.
· Low Output Ripple: Output capacitors and careful design reduce voltage ripple, protecting sensitive electronics.
· Built-in Protection: Many modules include overcurrent, overvoltage, thermal shutdown, and short-circuit protections.
Common Applications of Boost Power Modules
· Battery-Powered Devices: Smartphones, tablets, wearables, and portable medical devices use boost modules to step up battery voltage for internal circuits.
· Renewable Energy Systems: Solar panels often produce low and fluctuating voltages; boost modules increase voltage for battery charging or grid tie-in.
· Electric Vehicles: Boost converters raise battery voltage to levels needed by motors, power steering, or auxiliary systems.
· LED Lighting: Provides constant current and voltage for LED arrays, ensuring consistent brightness.
· Telecommunications: Powers RF amplifiers, base stations, and network equipment requiring higher voltages.
· Sensor Systems: Supplies stable voltages to analog-to-digital converters and other sensitive components in remote or battery-powered sensors.
Design Considerations
· Inductor Selection: Must handle peak currents without saturation and have low resistance to minimize losses.
· Switching Frequency: Higher frequencies reduce inductor and capacitor size but can increase switching losses and EMI.
· Duty Cycle Limits: Practical duty cycles rarely exceed 70–80% due to parasitic losses and efficiency drop-offs.
· Thermal Management: Efficient heat dissipation is critical for reliability, especially at high currents.
· EMI Mitigation: Proper layout and filtering reduce electromagnetic interference for compliance with standards.
Boost power modules are vital components in modern electronics, enabling devices to operate efficiently from lower voltage sources by stepping up voltage with high efficiency and reliability. Their compact size, integrated protections, and adaptability make them indispensable in applications ranging from consumer electronics to industrial and automotive systems.
For expert guidance on selecting and integrating boost power modules into your design, contact our technical support team or explore our product catalog.