Comprehensive Guide to Integrated Power Modules: DC-DC Power Module and Power Converter Module Solutions
May 15,2025
By:Epoch
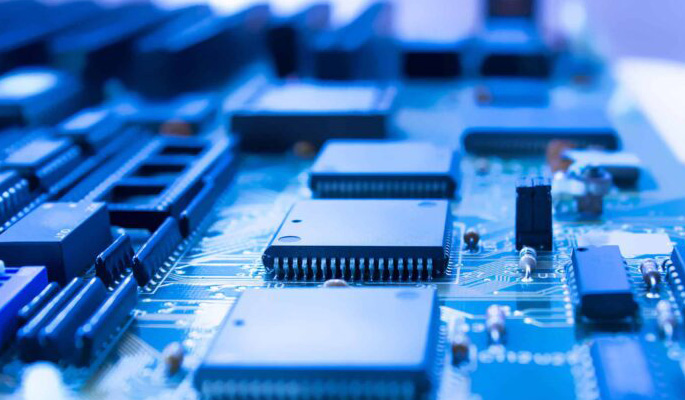
Integrated power modules are essential components in modern electronics, providing efficient, compact, and reliable solutions for voltage regulation and power conversion. As electronic devices become more sophisticated and space-constrained, the demand for advanced DC-DC power modules and power converter modules continues to rise. This article explores the landscape of integrated power modules, analyzing their input and output voltage ranges, form factors, and key applications based on the latest product matrix.
What is an Integrated Power Module?
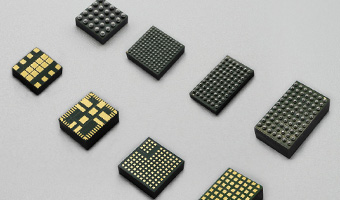
An integrated power module combines multiple power management functions into a single, compact package. These modules are designed to simplify power supply design, reduce board space, and improve overall system efficiency. The most common type is the DC-DC power module, which converts one DC voltage level to another, enabling devices to operate reliably across a wide range of input voltages.
DC-DC Power Module: Versatility Across Voltage Ranges
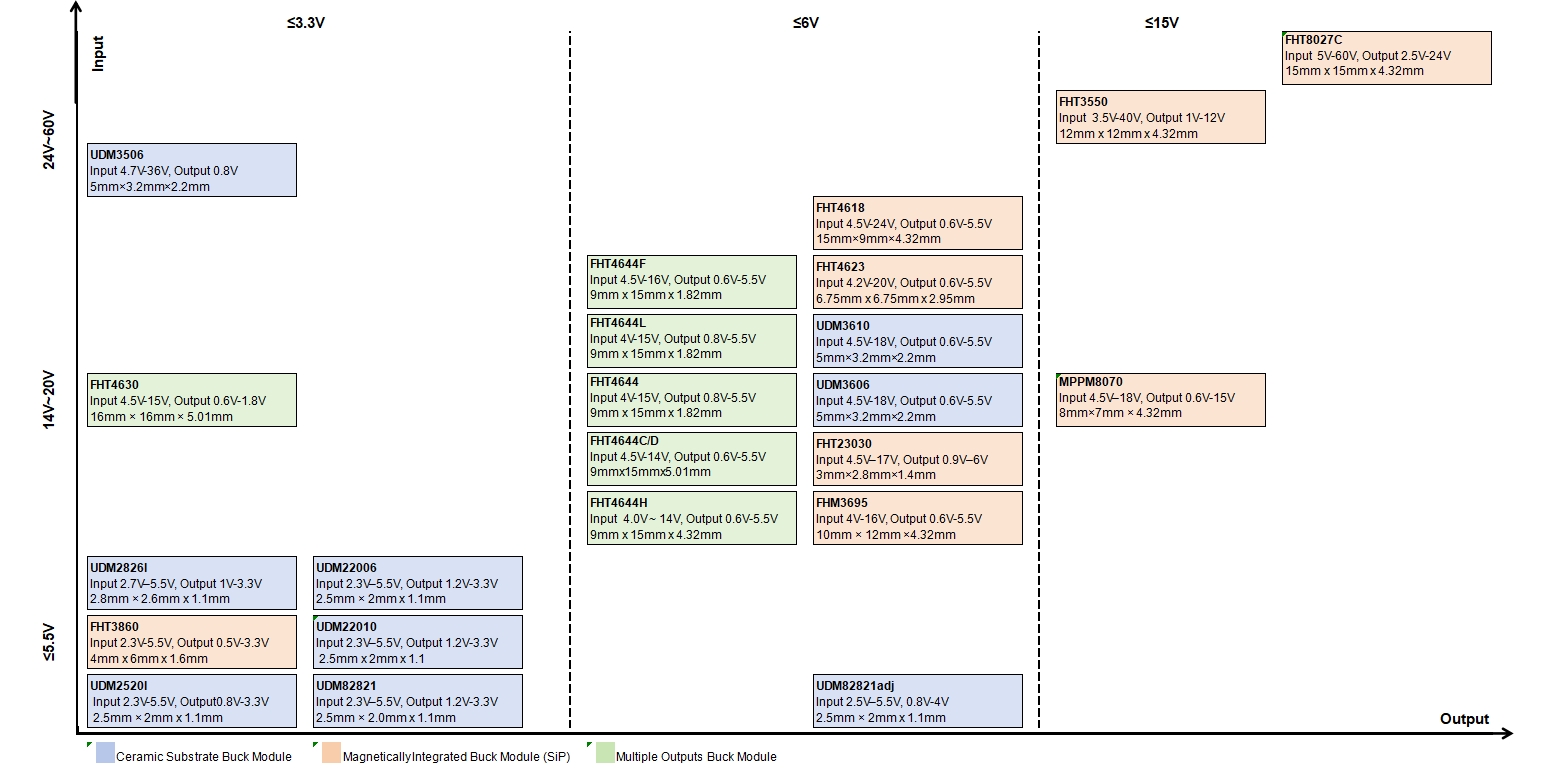
The product matrix reveals a broad selection of DC-DC power modules, each optimized for specific input and output voltage requirements:
· Low Voltage Input (≤5.5V):
Modules such as UDM2826I, UDM22006, and FHT3860 operate with input voltages as low as 2.3V, delivering output voltages from 0.8V to 3.3V. These compact modules (as small as 2.5mm x 2mm x 1.1mm) are ideal for portable electronics and battery-powered devices.
· Mid Voltage Input (14V–20V):
Solutions like FHT4630 and FHT4644F support higher input voltages (up to 15V or 16V) and deliver output voltages ranging from 0.6V to 1.8V or 5.5V. These modules are suitable for industrial systems and communication equipment that require stable, low-voltage outputs from higher input sources.
· High Voltage Input (24V–60V):
For applications demanding even higher input voltages, modules such as UDM3506 and FHT8027C can handle up to 60V, providing outputs from 0.8V to 24V. These are crucial for automotive, telecom, and industrial power systems.
Power Converter Module: Types and Technologies
The matrix categorizes modules by substrate and integration technology:
Module Type | Color Code in Matrix | Typical Applications |
Ceramic Substrate Buck Module | Blue | High efficiency, thermal stability |
Magnetically Integrated Buck Module (SiP) | Green | Ultra-compact, integrated magnetics |
Multiple Outputs Buck Module | Orange | Systems needing multiple regulated outputs |
Power converter modules are available in both single-output and multiple-output configurations, supporting diverse system architectures. Magnetically integrated modules (SiP) offer significant size reduction and improved EMI performance, making them attractive for space-constrained designs.
Choosing the Right DC-DC Power Module
When selecting a DC-DC power module or power converter module, consider the following:
· Input Voltage Range: Match the module to your system’s available input voltage.
· Output Voltage and Current: Ensure the module delivers the required output voltage and current for your load.
· Form Factor: Compact modules are essential for portable or densely packed systems.
· Thermal Performance: Ceramic substrate modules are ideal for applications with high thermal demands.
Applications of Integrated Power Modules
Integrated power modules are widely used in:
· Consumer electronics (smartphones, tablets)
· Industrial automation
· Telecommunications
· Automotive electronics
· Embedded computing systems
Integrated power modules, including DC-DC power modules and power converter modules, are the backbone of efficient, reliable, and compact power management in modern electronic systems. By understanding the input/output voltage requirements and available module technologies, engineers can select the optimal solution for their application, ensuring performance, efficiency, and space savings.